Insulation materials play a crucial role in maintaining energy efficiency and comfort in buildings. With advancements in technology and a growing focus on sustainability, the market offers a wide range of insulation materials to suit various applications. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the different types of insulation materials available today, exploring their unique properties, applications, and environmental impact.
- Fiberglass Insulation:
Fiberglass insulation is one of the most common and widely used types of insulation. Composed of fine glass fibers, it offers excellent thermal resistance and sound absorption properties. Fiberglass insulation is available in batts, rolls, or loose-fill forms, making it suitable for both residential and commercial applications. Its affordability, fire resistance, and easy installation make it a popular choice. - Cellulose Insulation:
Made from recycled paper products, cellulose insulation is an environmentally friendly option. It provides effective thermal insulation and soundproofing capabilities. Cellulose insulation is typically blown into wall cavities or attics, filling gaps and creating a seamless barrier against heat transfer. Its high recycled content and low embodied energy make it an attractive choice for eco-conscious consumers. - Spray Foam Insulation:
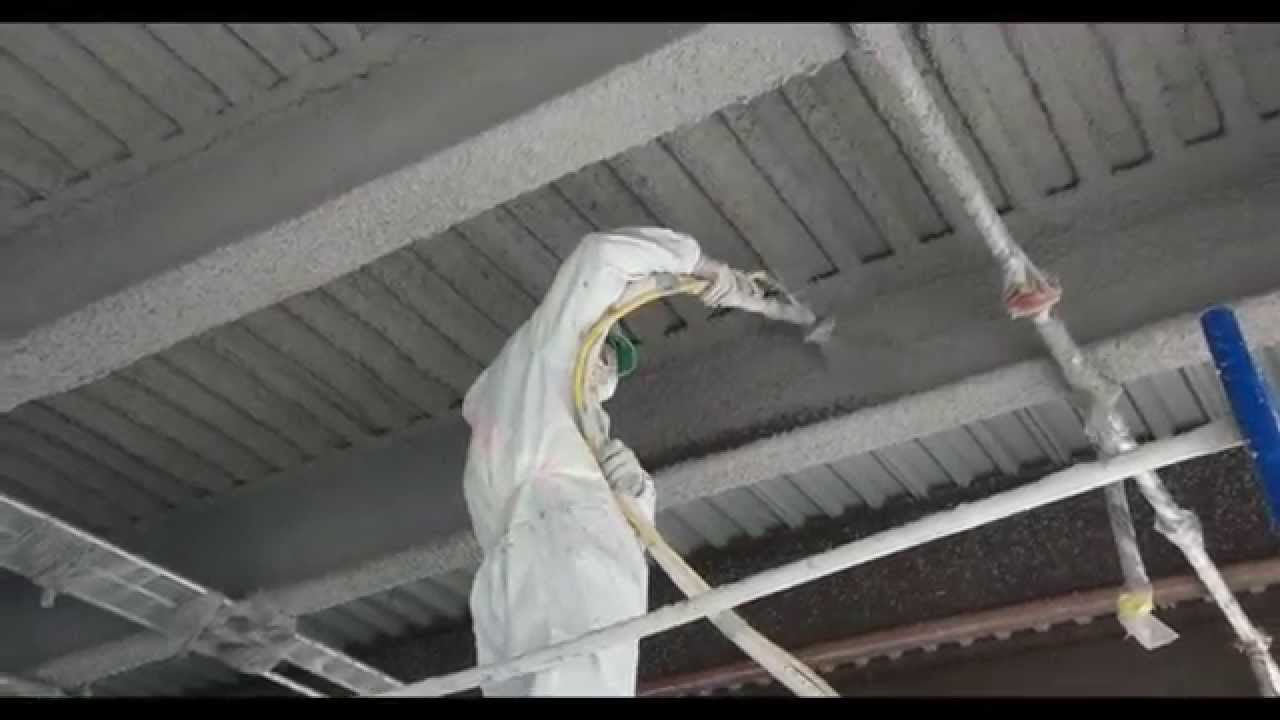
Spray foam insulation is a versatile material that expands upon application, filling gaps and creating an airtight seal. It offers exceptional thermal insulation and effectively reduces air leakage, making it highly energy-efficient. Spray foam insulation can be applied to various surfaces, including walls, roofs, and foundations. However, it requires professional installation due to its chemical composition and specialized equipment. - Mineral Wool Insulation:
Mineral wool insulation, also known as rock wool or slag wool, is made from natural or recycled minerals, such as basalt or slag. It provides excellent fire resistance, sound absorption, and thermal insulation properties. Mineral wool insulation is available in batts, boards, or loose-fill forms, catering to different construction needs. Its durability, moisture resistance, and non-combustible nature make it suitable for both residential and industrial applications. - Polyurethane Foam Insulation:
Polyurethane foam insulation is a high-performance material known for its exceptional thermal resistance. It is commonly used in spray foam form, expanding to fill cavities and creating a seamless barrier against heat transfer. Polyurethane foam insulation offers superior energy efficiency and can contribute to significant energy savings over time. However, it is important to consider its environmental impact, as some formulations may contain blowing agents with high global warming potential. - Aerogel Insulation:
Aerogel insulation is a cutting-edge material with remarkable thermal properties. Composed of a gel-like substance, aerogel is extremely lightweight and has an incredibly low thermal conductivity. It is often used in thin panels or blankets to provide superior insulation in space-constrained applications. Aerogel insulation is highly effective but tends to be more expensive compared to other insulation materials.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right insulation material is crucial for optimizing energy efficiency, comfort, and sustainability in buildings. This comprehensive guide has explored various types of insulation materials, including fiberglass, cellulose, spray foam, mineral wool, polyurethane foam, and aerogel. Each material offers unique properties and benefits, catering to different construction requirements. By understanding the characteristics and applications of these insulation materials, individuals and professionals can make informed decisions to create energy-efficient and environmentally friendly spaces.






+ There are no comments
Add yours